The manufacturing landscape is undergoing a profound transformation. Smart Manufacturing Factories represent the convergence of digital technologies, data analytics, and traditional manufacturing processes to create more efficient, flexible, and responsive production environments. As we navigate Industry 4.0, manufacturers who embrace these intelligent systems gain significant competitive advantages through enhanced productivity, reduced costs, and improved quality control. This comprehensive guide explores how smart manufacturing is reshaping the industrial sector and provides actionable insights for your own digital transformation journey.

What is Smart Manufacturing and Why Does It Matter?
Smart manufacturing represents the seamless integration of advanced technologies with manufacturing processes to create highly efficient, connected, and adaptive production systems. At its core, it’s about leveraging data, automation, and intelligent systems to optimize every aspect of the manufacturing process.
In the context of Industry 4.0, smart manufacturing factories serve as the physical manifestation of the fourth industrial revolution. Unlike traditional manufacturing facilities that operate in relatively isolated environments with limited connectivity, smart factories function as interconnected ecosystems where machines, systems, and humans communicate and collaborate in real-time.
The significance of smart manufacturing extends beyond mere technological advancement. It represents a fundamental shift in how products are conceived, designed, produced, and delivered to customers. This transformation is driven by the need to address several pressing challenges facing the manufacturing sector:

Global Competition
Manufacturers face intense pressure to reduce costs while improving quality and speed to market. Smart manufacturing provides the tools to achieve these seemingly contradictory goals simultaneously.
Customer Expectations
Today’s customers demand greater customization, faster delivery, and higher quality at competitive prices. Smart factories enable the flexibility to meet these diverse requirements efficiently.
Workforce Challenges
With skilled labor shortages affecting many regions, smart manufacturing technologies help maximize workforce productivity and create new roles that attract digital talent.
Key Technologies Enabling Smart Manufacturing Factories
The transformation to smart manufacturing is powered by a suite of complementary technologies that work together to create intelligent, connected production environments. Understanding these core technologies is essential for any manufacturer looking to embark on their smart factory journey.

Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT forms the foundation of smart manufacturing by connecting machines, products, and systems through networks of sensors that collect and exchange data. These sensors monitor everything from equipment performance and environmental conditions to product quality and inventory levels.
According to Deloitte’s 2025 Smart Manufacturing Survey, 46% of manufacturers are already leveraging industrial IoT solutions, with an additional 27% planning to invest in IIoT within the next 24 months.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning algorithms analyze the vast amounts of data generated in smart factories to identify patterns, predict outcomes, and optimize processes. These technologies enable predictive maintenance, quality control, and autonomous decision-making.
The implementation of AI in manufacturing is growing steadily, with 29% of manufacturers using AI/ML at the facility level and 24% deploying generative AI, according to recent industry surveys.
Robotics and Automation
Advanced robotics, including collaborative robots (cobots) that work alongside humans, automate repetitive, dangerous, or precision-requiring tasks. Modern robots are increasingly flexible, able to be reprogrammed quickly to handle different products or processes.
Physical automation ranks as a top investment priority for 37% of manufacturers in the next two years, highlighting its critical role in smart factory implementations.
Cloud Computing
Cloud platforms provide the scalable computing power and storage needed to process the enormous volumes of data generated in smart factories. They also enable remote monitoring, management, and collaboration across global manufacturing networks.
Currently, 57% of manufacturers are using cloud computing, with an additional 29% planning to invest in cloud technologies within the next 24 months.
Big Data Analytics
Advanced analytics tools transform raw data into actionable insights that drive continuous improvement. From real-time dashboards to complex simulation models, these tools help manufacturers optimize everything from equipment performance to supply chain logistics.
Data analytics is being leveraged by 57% of manufacturers, with 40% ranking it as their first or second highest priority for investment in the coming years.
Digital Twins
Digital twins create virtual replicas of physical assets, processes, or entire factories. These digital models enable simulation, testing, and optimization in a virtual environment before implementation in the real world, reducing risk and accelerating innovation.
The digital twin technology is increasingly being adopted for planning, startup, and ongoing optimization of automated systems, providing significant time and cost savings.
Augmented Reality (AR)
AR overlays digital information onto the physical environment, assisting workers with complex assembly, maintenance, and quality inspection tasks. AR can display step-by-step instructions, highlight components, and provide real-time feedback to improve accuracy and efficiency.
5G Connectivity
The high-speed, low-latency capabilities of 5G networks enable real-time communication between machines, systems, and humans. This is particularly important for applications requiring immediate response, such as autonomous vehicles or collaborative robotics.
Approximately 42% of manufacturers are already leveraging 5G technology to enhance connectivity in their smart factory implementations.
Cybersecurity
As manufacturing becomes more connected, robust cybersecurity measures are essential to protect sensitive data, intellectual property, and operational technology from threats. This includes network security, access controls, encryption, and continuous monitoring.
Manufacturers are dedicating an average of 15.74% of their IT budget to cybersecurity, recognizing its critical importance in smart factory environments.
Benefits of Implementing Smart Manufacturing Systems
The transition to smart manufacturing delivers numerous advantages that directly impact a company’s bottom line, operational efficiency, and competitive positioning. Understanding these benefits helps build the business case for investment in smart factory technologies.
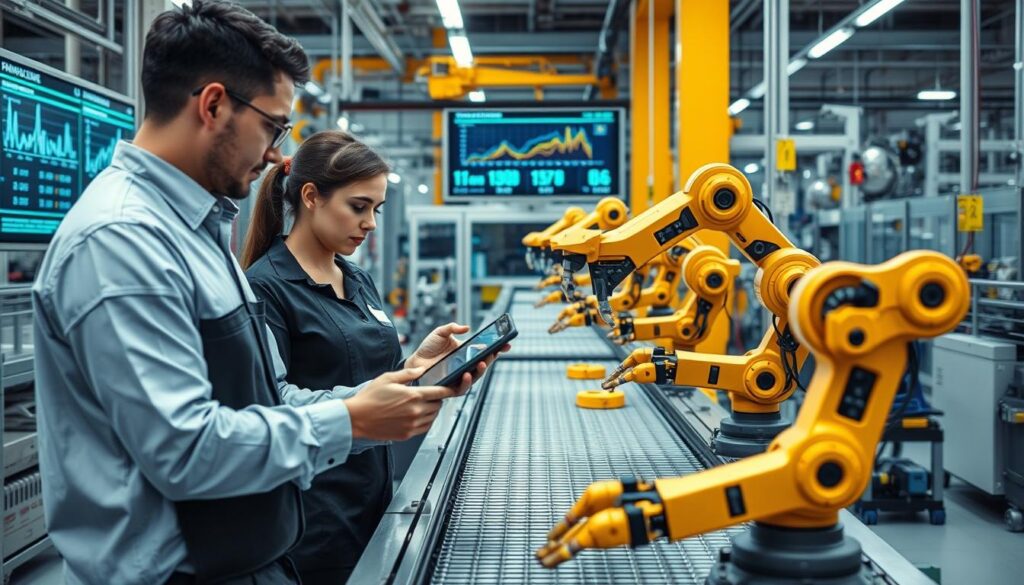

Key Benefits of Smart Manufacturing
- Increased Operational Efficiency: Smart factories report 10-20% improvement in production output and 7-20% improvement in employee productivity through optimized processes and reduced downtime.
- Enhanced Product Quality: Real-time monitoring and AI-driven quality control reduce defects, with some implementations achieving defect rates as low as 0.0012%.
- Production Flexibility: Rapid reconfiguration of production lines enables manufacturers to quickly adapt to changing market demands and produce customized products efficiently.
- Reduced Costs: Predictive maintenance reduces unplanned downtime by up to 50%, while optimized processes minimize waste, energy consumption, and labor costs.
- Improved Decision-Making: Data-driven insights enable faster, more informed decisions at all levels of the organization, from the shop floor to the executive suite.
- Enhanced Worker Safety: Automation of dangerous tasks and real-time monitoring of environmental conditions create safer working environments.
- Sustainability: Optimized resource utilization and reduced waste contribute to more environmentally sustainable manufacturing operations.
“The magic word for the future is ‘demand-driven production’. Today more than ever, consumers want their goods to be customized according to their wishes, which is why items are now mainly produced as needed. In order to supply these new production lines, dynamic systems are needed with stronger integration and interconnection between production and logistics.”
Ready to Start Your Smart Manufacturing Journey?
Download our comprehensive implementation guide to learn the step-by-step process for transforming your manufacturing operations.
Real-World Examples of Successful Smart Factory Implementations
Examining successful smart manufacturing implementations provides valuable insights into best practices, challenges, and potential outcomes. These case studies demonstrate how companies across various industries have leveraged smart factory technologies to achieve tangible business results.

Siemens Amberg Electronics Plant
Siemens’ Amberg facility represents one of the most advanced smart factories in operation today. By integrating physical manufacturing with digital technologies, Siemens has achieved remarkable results:
- 99.9988% production quality (defect rate of just 0.0012%)
- 8x increase in production volume without significant expansion
- Production of 15 million Simatic products annually
- Capability to manufacture over 1,000 different product variants
Key to their success has been the integration of real and virtual worlds, direct communication between products and machines, and sophisticated IT systems that optimize all production processes.
Bosch Homburg Plant
Bosch’s factory in Homburg, Germany, transformed its hydraulic valve production line through Industry 4.0 solutions to improve efficiency while maintaining flexibility. Their implementation included:
- Autonomous intelligent workstations capable of quick product switching
- Active Assist assembly technology with pick-to-light systems
- RFID integration for real-time component tracking
- Customized worker assistance based on qualification level
The results were impressive: setup time reduction from 450 seconds to zero, inventory days halved, 8% decrease in cycle times, and €500,000 in cost savings in the first year alone.
L3Harris Technologies
L3Harris Technologies established a Smart Manufacturing Cell at their Rochester, NY facility to meet increased customer demand for tactical radios. Their implementation featured:
- Augmented reality for real-time work instructions
- Common Industry 4.0 platform integrating vision inspection and precision tools
- Line-agnostic stations capable of building different products
- Comprehensive data collection and analysis systems
The results included the ability to run three product lines simultaneously with increased efficiency, reduced non-value-added time, improved cognitive ergonomics, and better space utilization and safety.
| Company | Industry | Key Technologies | Primary Benefits | ROI Timeframe |
| Siemens | Electronics | Digital twins, automation, IoT | Quality improvement, production volume increase | 2-3 years |
| Bosch | Automotive components | RFID, pick-to-light, worker assistance | Setup time reduction, inventory optimization | 1 year |
| L3Harris | Defense electronics | Augmented reality, vision inspection, data analytics | Efficiency, flexibility, quality control | 1-2 years |
| Magna | Automotive | Automation, intelligent software | Faster parts availability, reduced internal transport | 2 years |
| Fronius | Welding equipment | Autonomous mobile robots | Automated production supply, flexible transport | 1-2 years |
Challenges and Considerations for Adopting Smart Manufacturing
While the benefits of smart manufacturing are compelling, the transformation journey presents several challenges that manufacturers must address to ensure successful implementation. Understanding these challenges helps organizations develop effective strategies to overcome them.

Implementation Challenges
- High Initial Investment: Smart manufacturing technologies require significant capital expenditure, with 78% of manufacturers allocating more than 20% of their improvement budget to these initiatives.
- Integration Complexity: Connecting legacy systems with new technologies creates technical challenges, particularly in older facilities with limited digital infrastructure.
- Workforce Skills Gap: There’s a significant shortage of talent with the necessary digital skills, with 48% of manufacturers reporting moderate to significant challenges in filling production and operations management roles.
- Cybersecurity Risks: Increased connectivity exposes manufacturing systems to potential cyber threats, with 55% of manufacturers citing unauthorized access as a high concern.
- Change Management: Transitioning to new ways of working requires careful change management to overcome resistance and ensure adoption.
Strategic Considerations
- Phased Implementation: Rather than attempting a complete transformation at once, successful manufacturers typically adopt a staged approach, starting with high-impact, lower-risk initiatives.
- Clear Business Case: Each smart manufacturing investment should be tied to specific business outcomes with measurable KPIs to ensure ROI.
- Data Strategy: A comprehensive data strategy addressing collection, storage, analysis, and governance is essential for extracting value from smart manufacturing technologies.
- Talent Development: Building internal capabilities through training and recruitment is critical, with 53% of manufacturers using in-house training for executives and 43% leveraging vendor-provided training.
- Ecosystem Partnerships: Collaborating with technology providers, consultants, and academic institutions can accelerate implementation and provide access to specialized expertise.
Key Risk Mitigation Strategies
According to Deloitte’s 2025 Smart Manufacturing Survey, manufacturers are taking several approaches to mitigate risks associated with smart factory implementations:
- 68% performed a cybersecurity risk or maturity assessment of their smart manufacturing technology stack in the last year
- 72-74% conduct internal and external penetration testing and vulnerability assessments
- 52% have developed a central team or working group tasked with researching, developing, and deploying smart manufacturing initiatives
- 45% have developed a process to communicate to employees and customers the implications of smart manufacturing
- 44% have established a smart manufacturing center of excellence
Future Trends and Developments in Smart Manufacturing
The smart manufacturing landscape continues to evolve rapidly, with emerging technologies and approaches promising to further transform how products are designed, produced, and delivered. Understanding these trends helps manufacturers prepare for the future and make strategic investments that will remain relevant.

Industry 5.0: Human-Machine Collaboration
While Industry 4.0 focuses on connectivity and automation, Industry 5.0 emphasizes the collaborative potential between humans and machines. This next evolution recognizes that human creativity, problem-solving, and adaptability complement machine precision and consistency.
In this paradigm, robots handle monotonous and strenuous work while humans serve as “smart workers” who leverage their unique cognitive abilities for decision-making and complex assembly tasks. Technologies like collaborative robots and augmented reality will facilitate this partnership.
Sustainable Manufacturing
Environmental sustainability is becoming a central focus in smart manufacturing, driven by regulatory pressures, consumer expectations, and the business benefits of resource efficiency. Future smart factories will increasingly incorporate:
- Energy management systems that optimize consumption and utilize renewable sources
- Circular economy principles that minimize waste and maximize material reuse
- Carbon footprint tracking and reduction strategies embedded in production processes
- Water conservation and treatment technologies integrated into manufacturing operations
Distributed Manufacturing
The traditional model of large, centralized factories is evolving toward networks of smaller, more flexible facilities located closer to customers. This distributed approach offers several advantages:
- Reduced transportation costs and environmental impact
- Faster response to local market demands
- Greater resilience against supply chain disruptions
- Ability to customize products for regional preferences
Cloud-based manufacturing execution systems and standardized digital processes enable consistent quality across distributed facilities.
Advanced Materials and Processes
Smart manufacturing will increasingly incorporate advanced materials and novel production processes that enable new product capabilities and manufacturing efficiencies:
- Nanomaterials with unique properties for electronics, energy, and healthcare applications
- Biomanufacturing that uses biological systems to produce materials and products
- Multi-material 3D printing that creates complex, integrated components
- Self-healing materials that extend product lifecycles and reduce maintenance
Quantum Computing
As quantum computing matures, it will enable manufacturers to solve complex optimization problems that are currently intractable, such as:
- Supply chain optimization across thousands of variables and constraints
- Materials science simulations for developing new compounds with specific properties
- Complex quality control analysis that identifies subtle patterns in manufacturing data
- Production scheduling that maximizes efficiency across multiple interdependent processes
Autonomous Manufacturing Systems
The convergence of AI, robotics, and IoT is enabling increasingly autonomous manufacturing systems that can:
- Self-configure production lines based on incoming orders
- Automatically adjust parameters to optimize quality and efficiency
- Predict and prevent failures before they occur
- Coordinate complex multi-machine operations with minimal human intervention
These systems will reduce the need for routine human supervision while creating new roles focused on system design and exception handling.
Practical Steps for Manufacturers to Begin Their Smart Factory Transformation
Transforming traditional manufacturing operations into smart factories is a journey that requires careful planning, strategic investments, and organizational alignment. The following roadmap provides practical guidance for manufacturers at any stage of their smart manufacturing journey.
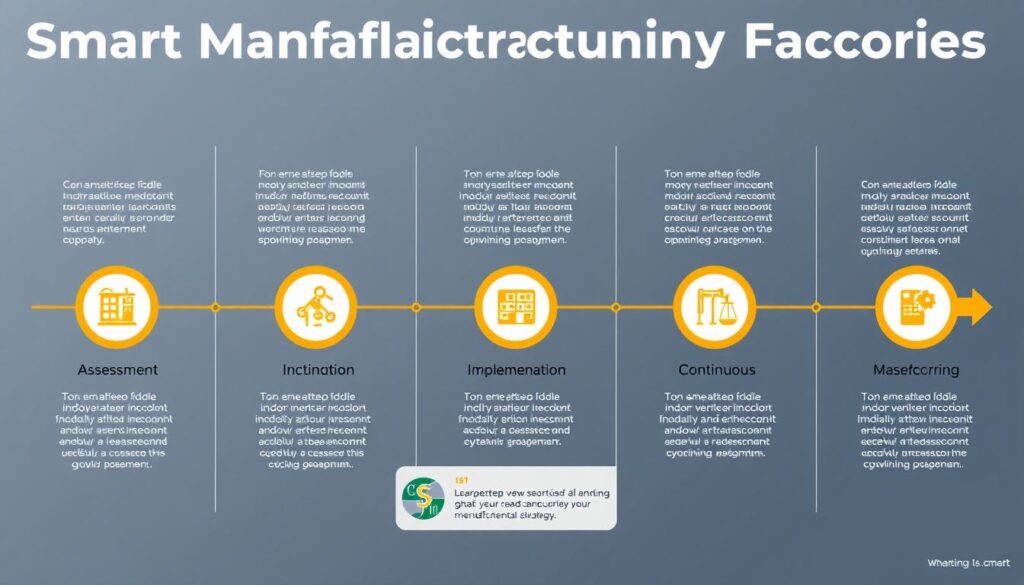
Phase 1: Assessment and Strategy Development
- Evaluate Current State
Conduct a comprehensive assessment of existing manufacturing operations, technology infrastructure, data capabilities, and workforce skills. Identify pain points, inefficiencies, and opportunities for improvement. - Define Clear Objectives
Establish specific, measurable goals for your smart manufacturing initiative, such as reducing downtime by 30%, improving quality by 25%, or increasing throughput by 15%. These objectives should align with broader business strategies. - Develop a Technology Roadmap
Create a phased implementation plan that prioritizes technologies based on potential impact, implementation complexity, and alignment with business objectives. Start with foundational capabilities like connectivity and data collection before moving to more advanced applications.
- Build the Business Case
Develop a detailed business case that quantifies the expected benefits, costs, and ROI of your smart manufacturing initiative. This should include both tangible benefits (cost savings, productivity improvements) and intangible benefits (enhanced agility, improved safety). - Secure Leadership Commitment
Gain executive sponsorship by demonstrating how smart manufacturing aligns with strategic priorities. Ensure leaders understand the transformational nature of the initiative and are prepared to provide sustained support.
Phase 2: Foundation Building
- Establish Connectivity Infrastructure
Implement the necessary network infrastructure to connect machines, sensors, and systems. This may include upgrading to industrial Ethernet, implementing wireless networks, and establishing edge computing capabilities. - Implement Data Collection and Management
Deploy sensors and data collection systems to capture information from manufacturing processes. Establish data management practices including storage, governance, and quality control. - Develop Analytics Capabilities
Build the capability to analyze manufacturing data for insights. Start with basic descriptive analytics before progressing to more advanced predictive and prescriptive approaches.
- Address Cybersecurity
Implement robust cybersecurity measures to protect connected manufacturing systems from threats. This should include network segmentation, access controls, encryption, and continuous monitoring. - Develop the Workforce
Invest in training programs to equip employees with the skills needed for smart manufacturing. This may include technical skills (data analysis, automation programming) and soft skills (digital literacy, problem-solving).
Phase 3: Implementation and Scaling
- Start with Pilot Projects
Implement small-scale pilot projects to test technologies, processes, and approaches. Focus on high-impact areas with clear success metrics and use these pilots to demonstrate value and learn lessons for broader deployment. - Implement Core Technologies
Based on your roadmap and pilot results, implement the core technologies that will drive your smart manufacturing transformation. This may include production execution systems, quality management systems, and automation solutions. - Integrate Systems and Data
Connect previously siloed systems to enable seamless data flow and process coordination. This may involve implementing middleware, APIs, or industrial IoT platforms to facilitate integration.
- Scale Successful Solutions
Expand successful pilot implementations across additional production lines, facilities, or business units. Apply lessons learned from pilots to improve implementation approaches and outcomes. - Manage Change Effectively
Implement a structured change management program to help employees adapt to new technologies and ways of working. This should include communication, training, and mechanisms to address concerns and resistance.
Phase 4: Continuous Improvement and Innovation
- Monitor and Measure Performance
Establish dashboards and reporting mechanisms to track key performance indicators and the impact of smart manufacturing initiatives. Use this data to identify areas for further improvement. - Foster a Culture of Innovation
Encourage experimentation and continuous improvement by establishing mechanisms for employees to suggest and implement new ideas. Recognize and reward innovative contributions to the smart manufacturing journey.
- Stay Current with Technology Trends
Continuously monitor emerging technologies and industry best practices. Evaluate new solutions for potential implementation as they mature and align with business needs. - Expand Ecosystem Partnerships
Develop relationships with technology providers, research institutions, and industry consortia to access expertise, share knowledge, and collaborate on innovation initiatives.
Implementation Success Factors
Research and experience from successful smart manufacturing implementations highlight several critical success factors:
- Cross-functional collaboration: Involve stakeholders from operations, IT, engineering, and business units in planning and implementation
- Data-driven decision making: Base investment and implementation decisions on data and measurable outcomes
- Agile approach: Use iterative implementation methods that allow for learning and adjustment
- Focus on people: Recognize that successful transformation depends as much on people and processes as on technology
- Long-term commitment: Maintain focus and investment over time, recognizing that transformation is a journey rather than a destination
Conclusion: The Future of Manufacturing is Smart
Smart Manufacturing Factories represent not just an evolution in production technology but a fundamental reimagining of how products are conceived, designed, manufactured, and delivered. By integrating digital technologies with physical processes, manufacturers can achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency, quality, and responsiveness.
The journey to smart manufacturing is challenging but essential for manufacturers who wish to remain competitive in an increasingly digital world. Those who successfully navigate this transformation will be rewarded with significant advantages: lower costs, higher quality, greater agility, and the ability to create innovative products and business models that were previously impossible.
As we look to the future, the convergence of technologies like AI, IoT, robotics, and advanced analytics will continue to expand the possibilities of smart manufacturing. The most successful manufacturers will be those who view smart manufacturing not as a one-time technology implementation but as an ongoing journey of continuous improvement and innovation.

Ready to Transform Your Manufacturing Operations?
Our team of smart manufacturing experts can help you develop a customized roadmap for your digital transformation journey. Schedule a consultation to discuss your specific challenges and opportunities.
Frequently Asked Questions About Smart Manufacturing Factories
What is the difference between a traditional factory and a smart factory?
Traditional factories operate with limited connectivity between machines and systems, rely heavily on manual processes and decision-making, and have minimal real-time visibility into operations. In contrast, smart factories feature comprehensive connectivity across all systems, utilize data and analytics for automated decision-making, implement advanced automation and robotics, and enable real-time monitoring and optimization of all processes. Smart factories are also characterized by their ability to adapt quickly to changing requirements and self-optimize their operations.
How much does it cost to implement a smart manufacturing system?
The cost of implementing smart manufacturing varies widely depending on the scope, existing infrastructure, and specific technologies deployed. Small-scale pilots might start at ,000-0,000, while comprehensive factory-wide transformations can require investments of millions of dollars. According to industry surveys, 78% of manufacturers allocate more than 20% of their overall improvement budget toward smart manufacturing initiatives. Rather than viewing this as a one-time capital expense, it’s more accurate to consider it an ongoing investment with returns realized through improved efficiency, quality, and agility over time.
How long does it take to implement a smart factory transformation?
Smart manufacturing is best viewed as a journey rather than a destination. Initial pilots can be implemented in 3-6 months, while more comprehensive transformations typically unfold over 2-5 years. Many manufacturers adopt a phased approach, starting with foundational capabilities like connectivity and data collection before progressing to more advanced applications. The timeline depends on factors including organizational readiness, existing infrastructure, available resources, and the complexity of manufacturing processes.
What skills are needed for smart manufacturing implementation?
Successful smart manufacturing requires a blend of traditional manufacturing expertise and digital skills. Key capabilities include data science and analytics, automation engineering, cybersecurity, systems integration, IoT implementation, and change management. Many manufacturers develop these capabilities through a combination of hiring, training existing employees, and partnering with external experts. According to recent surveys, 48% of manufacturers report moderate to significant challenges in filling production and operations management roles with the necessary digital skills.
How do smart factories impact the workforce?
Smart factories transform workforce requirements rather than simply reducing headcount. While some routine tasks may be automated, new roles emerge in areas such as data analysis, automation engineering, and systems integration. Workers often shift from manual tasks to monitoring, programming, and optimizing automated systems. This transition requires significant investment in training and skill development. According to industry research, 85% of manufacturers believe smart manufacturing initiatives will attract new talent to the industry by creating more engaging, technology-focused roles.
Transform Your IoT Vision Into Reality.
Get free expert insights, architectures & cost breakdowns.
Drop your email to schedule free meeting.